

pg 23
Night had fallen over the Crimean Peninsula
Crimea (Cry-me-uh), or the Autonomous Republic of Crimea, is a sub-national unit, an autonomous republic, of Ukraine. It is located on the northern coast of the Black Sea, occupying a peninsula of the same name.
The territory of Crimea was conquered and controlled many times throughout its history. The Cimmerians, Greeks, Scythians, Goths, Huns, Bulgars, Khazars, the state of Kievan Rus', Byzantine Greeks, Kipchaks, Ottoman Turks, Golden Horde Tatars and the Mongols all controlled Crimea in its early history. In the 13th century, it was partly controlled by the Venetians and by the Genovese; they were followed by the Crimean Khanate and the Ottoman Empire in the 15th to 18th centuries, the Russian Empire in the 18th to 20th centuries, Germany during World War II and the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic and later the Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic, within the Soviet Union in the rest of the 20th century.
Crimea is now an autonomous parliamentary republic which is governed by the Constitution of Crimea in accordance with the laws of Ukraine. The capital and administrative seat of the republic's government is the city of Simferopol, located in the center of the peninsula. Crimea's area is 26,200 square kilometres (10,100 sq mi) and its population was 1,973,185 as of 2007.
Crimean Tatars, an ethnic minority who now make up about 13% of the population, formed in Crimea in the late Middle Ages, after the Crimean Khanate had come into existence. The Crimean Tatars were forcibly expelled to Central Asia by Joseph Stalin's government. After the fall of the Soviet Union, some Crimean Tatars began to return to the region. A majority of the population is Crimean Russians, and the Russian language has official status in the autonomous republic.
God help those foolish enough to be caught afloat in the midst of a Black Sea storm.
The Black Sea is an inland sea bounded by Europe, Anatolia and the Caucasus and is ultimately connected to the Atlantic Ocean via the Mediterranean and Aegean Seas and various straits. The Bosphorus strait connects it to the Sea of Marmara, and the strait of the Dardanelles connects that sea to the Aegean Sea region of the Mediterranean. These waters separate eastern Europe and western Asia. The Black Sea also connects to the Sea of Azov by the Strait of Kerch.
The Black Sea has an area of 436,400 km2 (168,500 sq mi) (not including the Sea of Azov), a maximum depth of 2,212 m (7,257 ft), and a volume of 547,000 km3 (131,200 cu mi). The Black Sea forms in an east-west trending elliptical depression which lies between Abkhazia, Bulgaria, Georgia, Romania, Russia, Turkey, and Ukraine. It is constrained by the Pontic Mountains to the south, the Caucasus Mountains to the east and features a wide shelf to the northwest. The longest east-west extent is about 1,175 km.
Important cities along the coast include Batumi, Burgas, Constanța, Giresun, Hopa, Istanbul, Kerch, Kherson, Mangalia, Năvodari, Novorossiysk, Odessa, Ordu, Poti, Rize, Samsun, Sevastopol, Sochi, Sukhumi, Trabzon, Varna, Yalta and Zonguldak.
The Black Sea has a positive water balance; that is, a net outflow of water 300 km3 per year through the Bosphorus and the Dardanelles into the Aegean Sea. Mediterranean water flows into the Black Sea as part of a two-way hydrological exchange. The Black Sea outflow is cooler and less saline, and therefore floats over the warm, more saline Mediterranean inflow, leading to a significant anoxic layer well below the surface waters. The Black Sea also receives river water from large Eurasian fluvial systems to the north of the Sea, of which the Don, Dnieper and Danube are the most significant.
In the past, the water level has varied significantly. Due to these variations in the water level in the basin the surrounding shelf and associated aprons have sometimes been land. At certain critical water levels it is possible for connections with surrounding water bodies to become established. It is through the most active of these connective routes, the Turkish Straits, that the Black Sea joins the world ocean. When this hydrological link is not present, the Black Sea is a lake, operating independently of the global ocean system. Currently the Black Sea water level is relatively high, thus water is being exchanged with the Mediterranean. The Turkish Straits connect the Black and Aegean Seas and comprise the Bosphorus, the Sea of Marmara and the Dardanelles.
Climate
Short-term climatic variation in the Black Sea region is significantly influenced by the operation of the North Atlantic Oscillation, which is a term used to describe the climatic mechanisms resulting from the interaction between the north Atlantic and mid-latitude air masses.
While the exact mechanisms causing the North Atlantic Oscillation remain unclear, it is thought the climate conditions established in western Europe mediate the heat and precipitation fluxes reaching Central Europe and Eurasia, regulating the formation of winter cyclones, which are largely responsible for regional precipitation inputs and influence Mediterranean Sea Surface Temperatures (SST's). The relative strength of these systems also limits the amount of cold air arriving from northern regions during winter.
Other influencing factors include the regional topography, as depressions and storms systems arriving from the Mediterranean are funneled through the low land around the Bosphorus, Pontic and Caucasus mountain ranges acting as wave guides, limiting the speed and paths of cyclones passing through the region
Bondaruk had been born in 1960 in a village south of Ashgabat, Turkmenistan, high in the Kopet Dag Mountains.

Ashgabat (also Ashkhabad in transliteration from Russian (literally, Persian meaning: "City of Love") or formerly Poltoratsk between 1919–1927) is the capital and largest city of Turkmenistan, a country in Central Asia. It has a population of 695,300 (2001 census estimate), 2009 estimates around 1 million people in Ashgabat, and is situated between the Kara Kum desert and the Kopet Dag mountain range. Ashgabat has a primarily Turkmen population, with ethnic minorities of Russians, Armenians, and Azeris. It is 250 km from the second largest city in Iran, Mashhad.
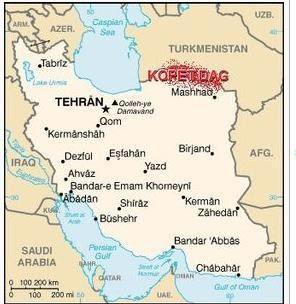
The Kopet Dag, Kopet Dagh, or Koppeh Dagh, also known as the Turkmen-Khorasan Mountain Range is a mountain range on the frontier between Turkmenistan and Iran, extending about 650 km (404 mi) along the border, east of the Caspian Sea. The highest peak of the range in Turkmenistan is southwest of the capital Ashgabat and stands at 2,940 m (9,646 ft). The highest Iranian summit is 3,191 m (10,466 ft).
This mountain range has a ski resort officially open by the former president of Turkmenistan Saparmurat Niyazov. Despite the lack of snow in the Kopet Dag mountains, Niyazov was determined to build a major resort there.
No comments:
Post a Comment